EGF
What is human EGF (Epidermal Growth Factor)
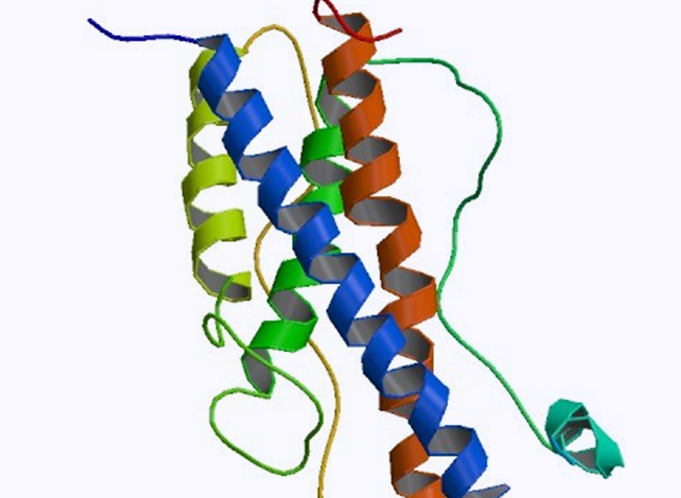
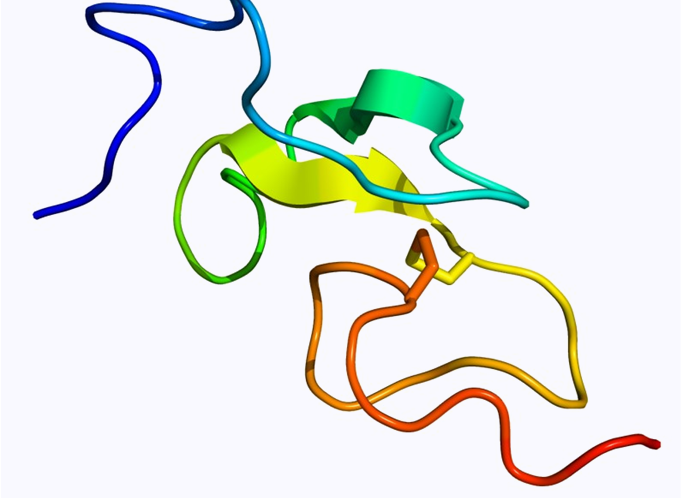
- EGF is a low-molecular-weight polypeptide with 53-amino acid residues.
- EGF participates in regulation of growth, proliferation, differentiation, and survival of skin epithelial cells.
- EGF induces epithelial development and promotes angiogenesis during wound healing process.
- In vitro, EGF is a mitogen for fibroblasts, epithelial and endothelial cells.
- We manufacture a human EGF equivalent starting from a chemically synthesized DNA using recombinant DNA technology and microbial fermentation.
- ED (human EGF equivalent; sh-Oligopeptide-1) in Clairesome-ED is encapsulated in a liposome-based carrier (Clairesome) for protein stability and skin hair follicular delivery.
hGH